LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Doi: 10.5578/tt.26305
Tuberk Toraks 2017;65(2):163-164

Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in an immunosuppressed child mimicking interstitial lung disease
Esra KARAKUŞ1, G?zin CİNEL2, Saliha KANIK Y?KSEK3, Belgin G?LHAN3
1 Clinic of Pathology, Ankara Children's Hematology Oncology Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
1 Ankara ?ocuk Sağlığı ve Hastalıkları Hematoloji Onkoloji Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi, Patoloji Kliniği, Ankara, T?rkiye
2 Clinic of Pediatric Chest Dieseases, Ankara Children's Hematology Oncology Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
2 Ankara ?ocuk Sağlığı ve Hastalıkları Hematoloji Onkoloji Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi, ?ocuk G?ğ?s Hastalıkları Kliniği, Ankara, T?rkiye
3 Clinic of Pediatric Infection Diseases, Ankara Children's Hematology Oncology Training and Research Hospital, Ankara Turkey
3 Ankara ?ocuk Sağlığı ve Hastalıkları Hematoloji Onkoloji Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi, ?ocuk İnfeksiyon Hastalıkları Kliniği, Ankara, T?rkiye
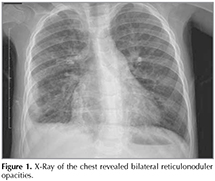
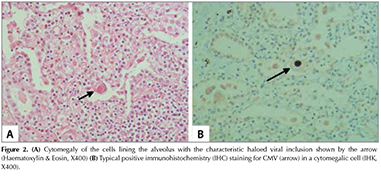
A 5-week-old female with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) presented with lower respiratory tract infection. X-Ray of the chest showed ground glassed opacities and multiple nodules evident in the left and right lung suggestive of an interstitial lung disease (Figure 1). Lung biopsy was performed. Hematoxylin and eosin stained sections showed areas of consolidation with numerous foamy histiocytes. Some of the alveolar spaces were lined by large cells, containing eosinophilic inclusion bodies (Figure 2A), surrounded by a characteristic halo which was positive for CMV immunohistochemical stain (Figure 2B). Histopathology of the lung biopsy showed CMV pneumonia. Clinical status improved after starting antiviral treatment. CMV pneumonia is one of the most important opportunistic pathogens in immunocompromised patients (1). CMV induced pulmonary lesions exhibit diffuse alveolar damage and/or interstitial inflammation and further prevent pulmonary interstitial fibrosis (2).
REFERENCES
- Cascio A, Iaria C, Ruggeri P, Fries W. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review. Int J Infect Dis 2012;16:474-9.
- Dong B, Wang Y, Wang G, Wang W, Zhou H, Fu Y. A retrospective study of cytomegalovirus pneumonia in renal transplant patients. Exp Ther Med 2014;7:1111-5.
Yazışma Adresi (Address for Correspondence)
Dr. Esra KARAKUŞ
Ankara ?ocuk Sağlığı ve Hastalıkları
Hematoloji Onkoloji Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesi,
Patoloji Kliniği, Ankara, T?rkiye
e-mail: esrakaraku@gmail.com
Geliş Tarihi/Received: 22.04.2016 - Kabul Ediliş Tarihi/Accepted: 19.06.2016